As the world marks diabetes awareness week Lucy Chege, founder of Nutrimedical Consultancy shares the right eating habits to help you prevent or manage diabetes.
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that affects body’s ability to produce or use insulin (type 1 Diabetes,type 2 Diabetes.)
When the body turns the food we eat into energy in form of sugar glucose, insulin is released to help transport energy to the cells. When the body produces little or no insulin, too much blood glucose remains in the blood and this means that blood sugar levels goes high than normal.
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to cardiovascular diseases, kidney disorders and other life threatening conditions.
Lifestyle causes of diabetes
Today’s family and individual menu predisposes everyone to diabetes due to poor food choices. Eating unhealthy diet, being overweight or obese, sedentary lifestyle plays a big role in developing this killer disease particularly type 2 diabetes.
To avoid taking in a lot of energy than you could expend, consult a nutritionist or doctor to know the amount of energy you require as different persons have different energy requirements depending on various factors. A person on construction site has higher energy needs compared to a person staying in the office the whole day.
BMI >25 kg/m2 is a risk factor for diabetes and this should be an alarm for dietary change and more physical activity.
Medical Nutrition Therapy.
Adapting a diabetic diet could be challenging at first, but your health should motivate you enough to walk the journey, you might fall or make a few mistakes in food choices but this should not worry you as long as you learn from your mistake.
Having diabetes does not mean going without foods you enjoy. The good news is that you can still eat your favorite foods, but you might need to eat smaller portions or enjoy them less often. The key to eating with diabetes is to eat a variety of healthy foods from all food groups, in the amounts your meal plan outlines.
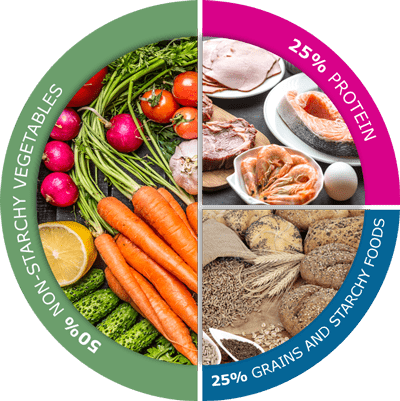
One should pay attention to the three food components: carbohydrates, protein and fats. The plate method and carbohydrate counting can help you control portion and size.
1. Carbohydrates.
These are energy giving foods and most blood sugar is made from them, thus failure to control them could have a huge effect on your glucose levels. Most carbohydrates come from starches, fruits, milk, and sweets. Try to limit carbohydrates with added sugars or those with refined grains, such as white bread and white rice. Instead, eat carbohydrates from fruit, vegetables, whole grains, beans, and low-fat or non-fat milk.
2. Proteins.
Lean meat, chicken or turkey without the skin, fish, eggs, nuts and peanuts dried beans and certain peas, such as chickpeas are good for a diabetic diet plan.
3. Fats.
Use oils when cooking food instead of butter, cream, shortening, lard, or stick margarine.
Eat foods with heart-healthy fats or oils that are liquid at room temperature, such as canola and olive oil, nuts and seeds, heart-healthy fish such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel, avocado.
Foods and drinks diabetic people should limit intake:
Fried foods and other foods high in saturated fat and trans- fat, foods high in salt, also called sodium, sweets, such as baked goods, candy, and ice cream, beverages with added sugars, such as juice, regular soda, and regular sports or energy drinks.
Drink water instead of sweetened beverages.
Plate method demo
½ plate=vegetables
¼ plate=lean meat or cereals
¼ plate=starch from
whole grains.
To manage your blood glucose, you need to balance what you eat and drink with physical activity and diabetes medicine, if you take any. What you choose to eat, how much you eat, and when you eat are all important in keeping your blood glucose level in the range.