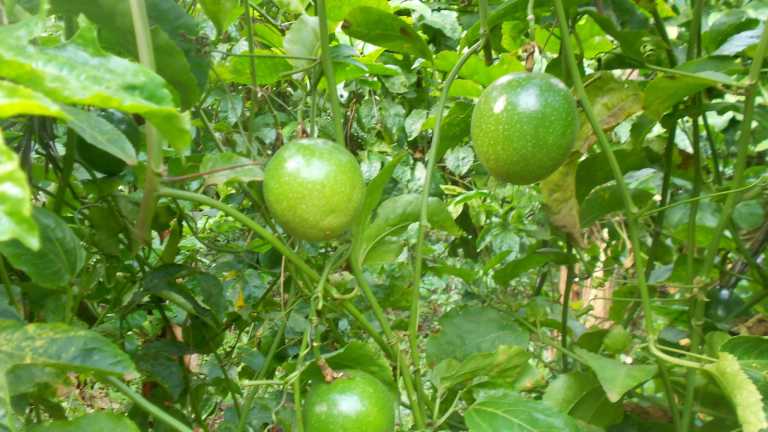
Growing passion fruits: What you need to know

Passion fruits grow best with soil nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium. The amounts of these nutrients vary at the various stages of growing.
You can add a soil conditioner such as humate. Application of the conditioner helps in soil enhancement, which allows the soil to quickly absorb of necessary nutrients.
If you used manure while planting, you are advised to add NPK (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) after a month. In the second month, use TSP (Triple Super Phosphate) or SSP (Single Super Phosphate). You can then interchange it with CAN (calcium ammonium nitrate), which helps in the fruit tissue development and strengthening of the cover of the fruit.
Once you give the plant good manure, at planting and after three months, you can start harvesting as early as after six months although poor manure distribution to the seedlings delays harvesting even up to nine months.
It is recommended to use the fertilisers (organic and inorganic) interchangeably.
Marketing
There are different buyers depending on the target market.
These different markets or buyers range from traders, wholesalers, retailers, hotels, restaurants, supermarkets and individual customers. Depending on availability of market that is where the farmer will sell. Prices range from Shs1,500 to Shs10,000 or more depending on the market.
Weeding
During land preparation, the garden must be free of weeds. After planting, introduce grass bands which should be kept short to prevent it from overgrowing. The dry grass can then used to mulch or feed animals.
If you decide to weed, do not leave the ground bare.
You can intercrop the passion fruits with strawberries. They are good cover crops, which help to keep the soil covered.
Storing
The fruits can stay for more than two weeks when stored in a place with room temperatures. It is advisable to apply CAN before harvesting so that the shelf life of the passion fruits is prolonged. However, for many local farmers, what is produced is sold immediately.
Care and management
Pests and diseases in passion fruits are a result of planting infected seedlings or using infected seeds, over cropping or transfer by animals from one place to another.
Here, Lydia Nantabo, an agronomist, notes some of the common pests and diseases that affect the fruit and can result in poor fruit quality and quantity.
Meet Naivasha’s Class 8 Drop-out Earning Millions From Breeding Dogs For Sale
Aphids: These are pear-shaped, soft bodied insects, with long legs and antennae and are usually green or yellow. They can appear dark or black with or without wings.
Aphids suck the sap, which causes curling or cupping of infected leaves. These insects spread the virus that is responsible for woodliness. Their excreta coats the leaves and prevents photosynthesis from taking place.