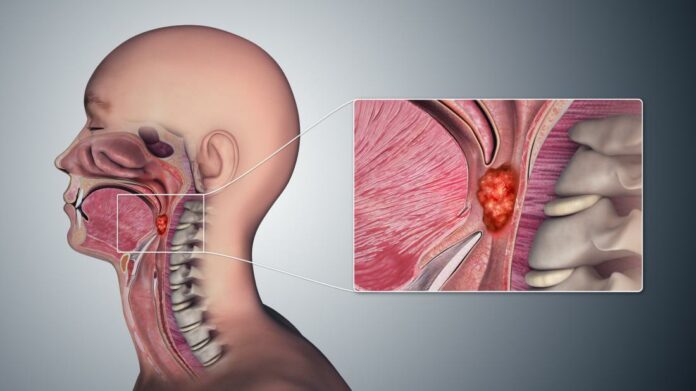
Throat cancer is often grouped into two categories: pharyngeal cancer and laryngeal cancer. Pharyngeal cancer forms in the pharynx (the hollow tube that runs from behind your nose to the top of your windpipe). Laryngeal cancer forms in the larynx (your voice box).
Signs
It can be difficult to detect throat cancer in its early stages. Common signs and symptoms of throat cancer include:
- a change in your voice
- trouble swallowing (dysphagia)
- weight loss
- sore throat
- constant need to clear your throat
- persistent cough (may cough up blood)
- swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- wheezing
- ear pain
- hoarseness
Causes and Risk Factors
Men are more likely to develop throat cancer than women. Certain lifestyle habits increase the risk of developing cancer of the throat. These include:
- smoking
- excessive alcohol consumption
- vitamin A deficiency
- exposure to asbestos
- poor dental hygiene
There is also a connection between throat cancer and certain types of human papillomavirus infections (HPV). This is a sexually transmitted virus. The Cancer Treatment Centers of America say HPV infection is a risk factor for both cervical cancers in women and throat cancer.
Throat cancer has also been linked to other types of cancers. In fact, some people diagnosed with throat cancer are diagnosed with esophageal, lung, or bladder cancer at the same time. This is typically because cancers often have the same risk factors, or because cancer that begins in one part of the body can spread throughout the body in time.
This is how much it really costs to treat a Covid-19 patient in Kenya
Diagnosis
To check for throat cancer, your doctor will perform a laryngoscopy or will refer you to a specialist who is trained to do these procedures. This procedure gives your doctor a closer view of your throat.
After you’re given a local anesthetic, your doctor inserts a long flexible tube down your throat, and uses a light and a mirror to examine your throat. If this test reveals abnormalities, your doctor may take a tissue sample from your throat (biopsy) and test the sample for cancer.
Staging
If your doctor finds cancerous cells in your throat, they will order additional tests to identify the stage, or the extent, of your cancer.
- Stage 0: The tumor has not invaded tissue beyond your throat.
- Stage 1: The tumor is less than 7 cm and limited to your throat.
- Stage 2: The tumor is slightly larger than 7 cm, but still limited to your throat.
- Stage 3: The tumor has grown and has spread to nearby tissues and organs.
- Stage 4: The tumor has spread to your lymph nodes and/or distant organs.
Your doctor can use a variety of tests to stage your throat cancer. Imaging tests like a CT scan or an MRI will allow your doctor to take a closer look at the chest, neck and head, giving them a better picture of the disease’s progression.
Treatment
Surgery
If the tumor in your throat is small, your doctor may surgically remove the tumor. This surgery would be done in the hospital while you are under sedation.
Radiation therapy
Following the removal of the tumor, your doctor may recommend radiation therapy. Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to destroy malignant cancer cells. It would target any cancerous cells left behind by the tumor.
Chemotherapy
In the case of large tumors and tumors that have spread to the lymph nodes and other organs or tissue, your doctor may recommend radiation, as well as chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is a drug that kills and slows the growth of malignant cells.